Describe the role of soil microbes decomposition and soil respiration in transferring carbon from the soil to the atmosphere. Changes that put carbon gases into the atmosphere result in warmer temperatures on Earth.
What Is The Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis Decomposition Respiration And Combustion Earth How
Carbon is a crucial element that shapes our todays environment and has a crucial role to play in the formation of the body of a living creature whether it be animal or plant.
. The Earths carbon reservoirs naturally act as both sources adding carbon to the atmosphere and sinks removing carbon from the atmosphere. Its one of the most important cycles of the earth which allows carbon to be recycled reused throughout the biosphere. A cycle diagram is a variation on the process diagram in which the process repeats itself.
Plants to make carbohydrates in photosynthesis. So its a good idea to make that point in your answer. Because some carbon gases are greenhouse gases changes in the carbon cycle that put more carbon in the atmosphere also warm Earths climate.
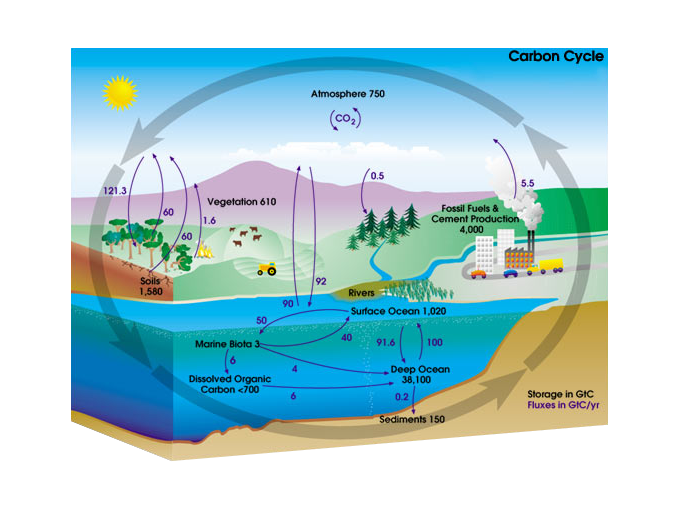
Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the land ocean and life through biological chemical geological and physical processes in a cycle called the carbon cycle. The water vapor eventually condenses forming tiny droplets in clouds. The diagram below illustrates the carbon cycle in nature.
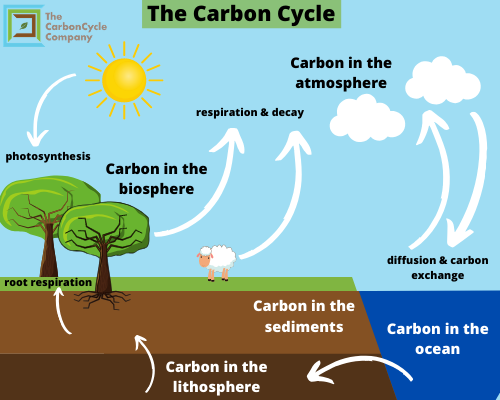
Although we will look at them separately its important to realize these cycles are linked. The carbon cycle is the system of biological and chemical processes that make carbon available to living things for use in tissue building and energy release Kinoshita 242. The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere pedosphere geosphere hydro - sphere and atmosphere of Earth.
Keeping Track of What You Learn Throughout these labs you will find three kinds of questions. Carbon is a constituent of all organic compounds many of which are essential to life on Earth. Where the carbon is located in the atmosphere or on Earth is constantly in flux.
Describe how carbon is stored in soil. Carbon cycle can be defined as the process where carbon compounds are interchanged among the biosphere geosphere pedosphere hydrosphere and atmosphere of the earth. Each Carbon is the fourth most affluent element in the universe and is an important part of most molecules that make up most of the worlds natural resources and organic matter which is why the carbon cycle is one of the most important.
A visible mass of water or ice particles suspended at a considerable altitude. Carbon is initially stored in the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. The key vehicle in which the processes of oxygen and carbon are related is plants.
The cycling of carbon between the land and atmosphere is known as the fast carbon cycle. This is the movement of carbon from living things up into the atmosphere. All living cells are composed of proteins consisting of carbon hydrogen oxygen and nitrogen in various combinations and each living organism puts these elements together according to its own.
The carbon cycle is a complex series of processes that occurs in the biosphere pedosphere geosphere hydrosphere atmosphere. It was mainly discovered by Joseph Priestley Antoine Lavoisier. They work independently but are dependent on each other since the carbon cycle releases oxygen for the usage of the oxygen cycle and the oxygen cycle emits carbon dioxide CO2 that goes back to the carbon cycle in turn.
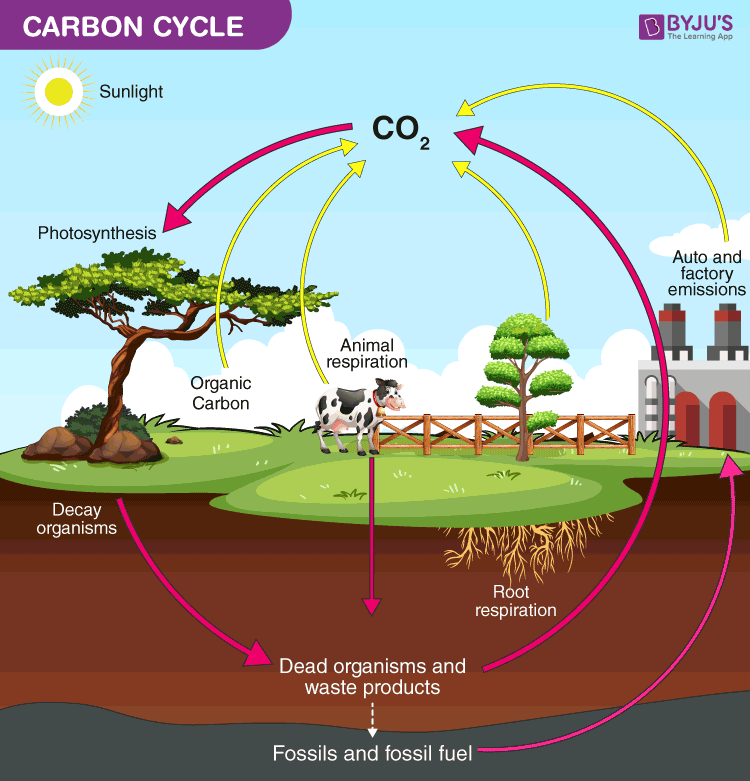
Carbon from the atmosphere moves to green plants by the process of photosynthesis and then to animals. By burning fossil fuels people are changing the carbon cycle with far-reaching consequences. Along a chain of processes is called a cycle the series of processes in which the carbon atom goes through is called the carbon cycle.
Now we shift gears in a major way away from climate physics you now have seen its main ingredients to the emergent miracle that is the carbon cycle on Earth. Since our planet and its atmosphere form a closed environment the amount of carbon in this system does not change. One dealing with long-term cycling of carbon through geologic processes.
A cycle of thermonuclear reactions in which four hydrogen atoms synthesize into a helium atom by the. Not only is carbon the chemical element of life it is also the means of storing lifes energy. 4 rows The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the.
Biosphere Atmosphere Geosphere and Hydrosphere. With carbon dioxide this takes place through the process of respiration from plants and animals and both CO2 and methane CH4 are released through the decomposition of plants and. This substance is absorbed by the photosynthetic.
Our forested areas and our oceans are carbon sinks. Describe the possible impact of a warming climate on permafrost carbon. One dealing with rapid carbon exchange among living organisms.
Write a 150-word description of this diagram for a university lecturer. Carbon cycle in biology circulation of carbon in various forms through nature. If all sources are equal to all sinks the carbon cycle can be said to be in equilibrium or in balance and there is no change in the size of the pools over time.
Interest in the carbon cycle. Carbon is a essential element for the living organisms and its economically important. By process of respiration and decomposition of dead organic matter it returns to the atmosphere.
Any change in the cycle that shifts carbon out of one reservoir puts more carbon in the other reservoirs. The carbon cycle begins with the process of photosynthesis which transforms inorganic carbon into organic carbon. The Water Cycle also known as the hydrologic cycle is the journey water takes as it circulates from the land to the sky and back again.
On the short time scale the carbon cycle is most visible in life. The source of the carbon found in living matter is carbon dioxide CO2 in the air or dissolved in water. The carbon cycle is most easily studied as two interconnected subcycles.
Carbon flows between the atmosphere land and ocean in a cycle that encompasses nearly all life and sets the thermostat for Earths climate. Up to 24 cash back Carbon enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide from respiration breathing and combustion burning. Algae and terrestrial green plants producers are the chief agents of carbon dioxide fixation through.
Along with the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle the carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events key to making Earth capable of sustaining life. Carbon cycle involves a continuous exchange of carbon between the atmosphere and organisms. The carbon cycle as the nitrogen cycle occurs in all the spheres.
Carbon flows between each reservoir in an exchange called the carbon cycle which has slow and fast components. Definition of carbon cycle. Carbon Cycle is a biogeochemical cycle where various carbon compounds are interchanged among the various layers of the earth namely the biosphere geosphere pedosphere hydrosphere and atmosphere.
We will look at how carbon cycles through the land the oceans and. The cycle of carbon in the earths ecosystems in which carbon dioxide is fixed by photosynthetic organisms to form organic nutrients and is ultimately restored to the inorganic state as by respiration protoplasmic decay or combustion 2. The Carbon Cycle Step 2 Carbon dioxide is absorbed by producers life forms that make their own food eg.
The carbon cycle describes the process in which carbon atoms continually travel from the atmosphere to the Earth and then back into the atmosphere.

0 Comments